How a steam locomotive works
The Engine Shed at the GCR
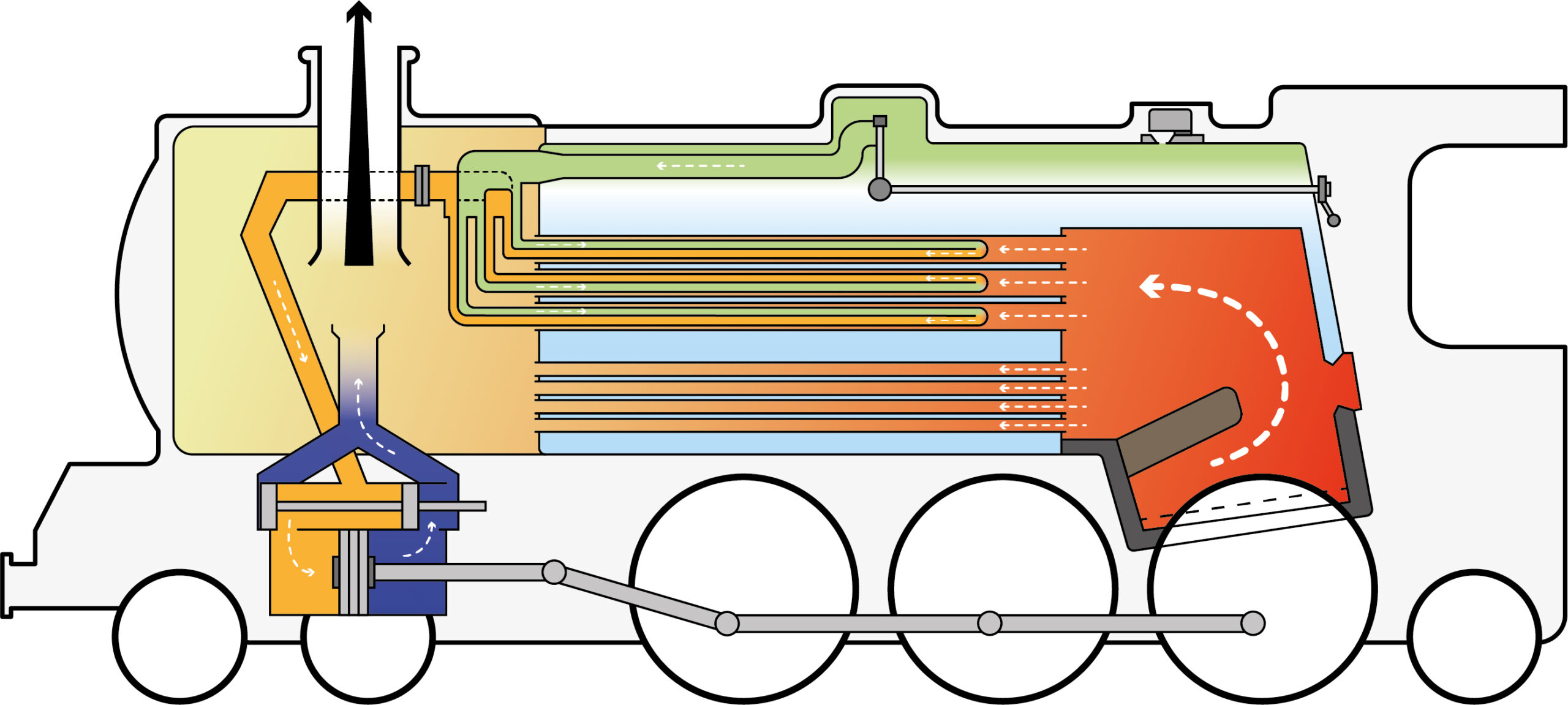
A steam locomotive operates by converting the energy from burning coal into mechanical motion.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
Process of conversion
Step 1
Combustion:
Coal is burned in the firebox, producing heat.
Step 2
Boiler:
The heat generated from the firebox turns water in the boiler into steam.
Step 3
Steam Pressure:
The high-pressure steam is directed into cylinders, where it pushes pistons back and forth.
Step 4
Cylinder and Pistons:
The high-pressure steam is directed into cylinders, where it pushes pistons back and forth.
Step 5
Connecting Rods and Wheels:
The pistons are connected to the locomotive’s driving wheels via connecting rods. As the pistons move, they turn the wheels.
Step 6
Exhaust:
After doing its work, the steam is released through the chimney, creating the characteristic exhaust sound.
Internal workings
Add Your Tooltip Text Here

